Reflection of the last weeks
-
Never had a pipette in hand before this - got feeling for how archaic following wetlab protocols per hand is
- Realized that robotic wetlab infrastructure is needed for high throughput research
-
Realized limitations of brain organoids
- Vascularization
- Maturation
- Blood brain barrier modeling
- Modeling of the lymbic system/stem brain - currently focused on prefrontal regions
-
Coming weeks:
- Researching differences between mouse/human brain
- Researching continuous hormone measurement systems
- In silico modeling of nootropic compounds
The bigger picture:
- 7 billion people drink caffeine
- 2 billion knowledge workers globally depend on cognitive enhancement
- Knowledge work hubs like the Bay Area, Boston/NYC & London are known for psychoactive drug usage
- Neurodiversity leads to creativity:
- Paul Erdős: Mathematical genius who relied on amphetamines for decades
- Francis Crick: Co-discoverer of DNA structure, reportedly used LSD
- Kary Mullis: Nobel Prize winner for PCR, advocated for LSD's cognitive benefits
- First banking houses being created around coffee houses in London (Lloyd's of London)
- ~700 substances show potential for brain health & cognitive enhancement
- Market opportunity: Knowledge workers represent the highest-value demographic globally
The problem: Feedback loops - current nootropic/supplement space is not personalized or data-driven
Current Issues:
- No personalized optimization: One-size-fits-all approach ignores genetic polymorphisms
- COMT gene variants affect dopamine metabolism (fast vs slow metabolizers)
- 5-HTTLPR serotonin transporter gene variations
- BDNF gene polymorphisms impact neuroplasticity
- Lack of real-time feedback: Users have no objective measures of cognitive improvement
- Poor dose optimization: No data on individual metabolic rates or receptor sensitivity
- Tolerance and adaptation: Brain's homeostatic mechanisms reduce effectiveness over time
- Questionable compound quality: Unregulated supplement industry with inconsistent purity
Markers we need to track:
- Neurotransmitter levels: Dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, acetylcholine
- Functional markers: Cerebral blood flow, glucose metabolism, neural oscillations
- Inflammatory markers: CRP, IL-6, TNF-α
- Neurotrophic factors: BDNF, NGF, GDNF
- Cognitive performance: Working memory, processing speed, attention span
- Metabolic markers: Blood glucose, lipid profiles, oxidative stress indicators
Using brain organoids to measure the effects of nootropic compounds
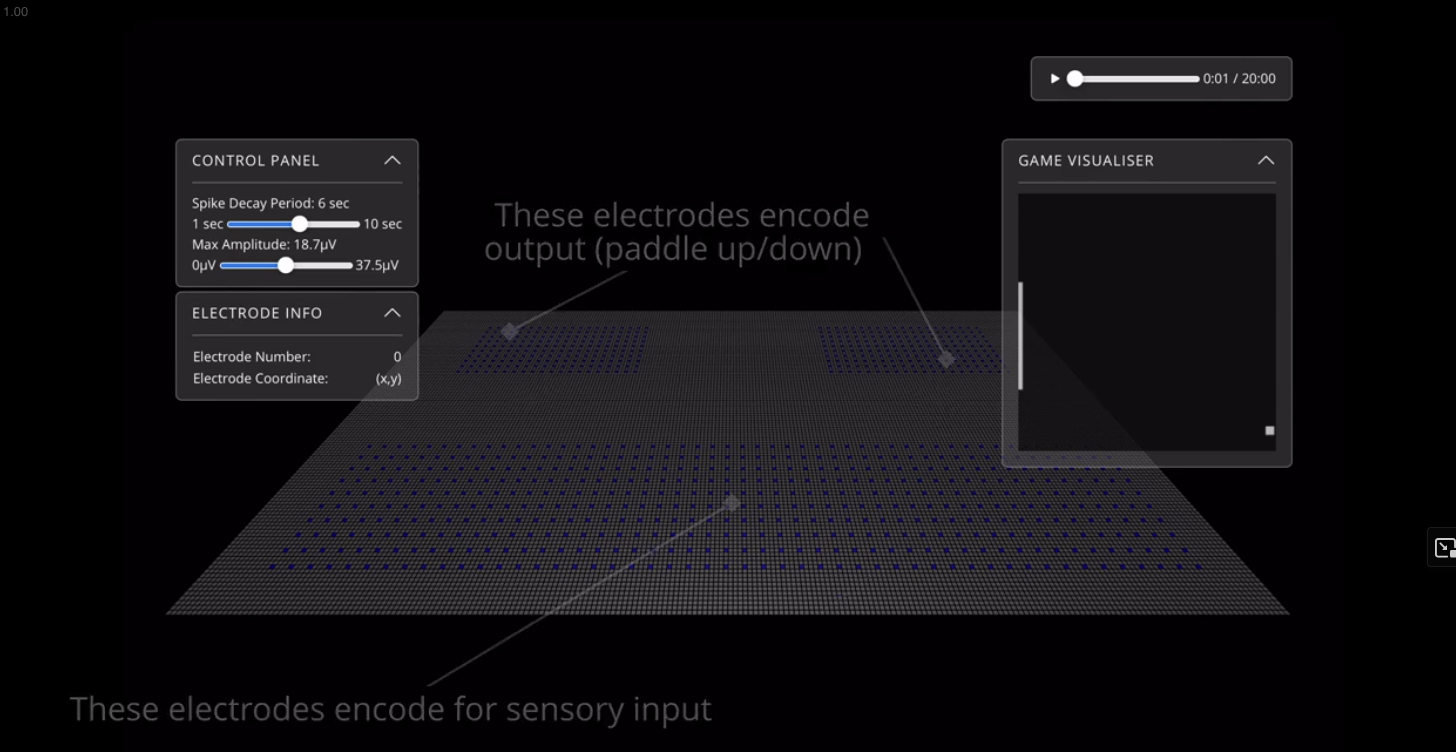
Methodology:
- iPSC-derived brain organoids: 4-month cultivation period reaching ~200,000 neurons
- Multi-electrode arrays (MEAs): Real-time electrical activity monitoring
- Compound injection protocols: Precise dosing using filtration systems
- High-throughput screening: Test 100+ compounds simultaneously
- Assembloids: Connected organoids modeling different brain regions
- Vascularized organoids: 3D-bioprinted blood vessels for improved nutrition
What we measure:
- Electrical activity: Action potential frequency, network synchronization
- Metabolic changes: Glucose consumption, oxygen utilization
- Neurotransmitter release: Real-time monitoring via biosensors
- Morphological changes: Dendritic growth, synaptic density
- Gene expression: RNA sequencing for pathway activation
Current challenges with brain organoids
Fundamental limitations (4-month organoids vs 21-year-old brain):
- Size: 2-4mm diameter vs 1,400g human brain
- Neuron count: 50K-200K vs 86 billion neurons
- Development stage: Equivalent to 14-24 week fetal brain
- No sleep / wake cycle: Substantial for learning / neuroplasticity in humans
- Missing cell types: Especially limited microglia
- No myelination: <1% vs >50% myelinated axons in adult brain
- Simplified neurotransmitter systems: Only 20-30% of adult complexity
- No blood-brain barrier: Overestimates drug penetration
- Missing brain regions: No hippocampus, basal ganglia, cerebellum
Specific nootropic screening limitations:
- Stimulants (Modafinil, Adderall): Require intact dopaminergic pathways
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: Limited without mature cholinergic innervation
- AMPA modulators: Reduced efficacy without complex dendritic processing
- Noradrenergic modulators: Virtually no target structures present
Algernon's Law
Should we interfere with evolutionary processes?
- Yes - provide energy and let systems overdrive: Use additional energy resources
- Evolutionary mismatch theory: Modern abundance vs ancient scarcity-adapted brains
- Precedent exists: Caffeine consumption shows 7 billion people already enhance cognition
- Optimization vs overclocking: Work within biological constraints, not against them
- Energy availability: Modern nutrition provides unprecedented metabolic resources
Evidence for enhancement potential:
- Genetic diversity: Natural cognitive variation shows improvement possibility
- Training effects: Brain plasticity demonstrates enhancement capacity
- Pharmacological precedent: Existing nootropics prove modifiability
- Nutritional optimization: Proper micronutrients already enhance performance
Neurotypes
Genetic-based personalization:
- COMT gene variants:
- Val/Val (fast metabolizers): Need higher dopamine doses
- Met/Met (slow metabolizers): Sensitive to overstimulation
- 5-HTTLPR polymorphism:
- Short allele: Higher anxiety, benefits from serotonergic support
- Long allele: Lower baseline anxiety, different optimization needs
- BDNF polymorphisms:
- Met carriers: Reduced neuroplasticity, need enhancement support
- Val/Val: Normal plasticity, standard protocols effective
Functional neurotypes:
- High stimulation seekers: Dopaminergic system optimization
- Anxiety-prone individuals: GABAergic and serotonergic support
- Creative types: Default mode network modulation
- Analytical thinkers: Frontal lobe optimization
- Memory-focused: Cholinergic system enhancement
Compounds case studies
- Lions Mane: Neurogenesis and dendritic growth - Mechanism: Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and BDNF stimulation
- Alpha-GPC: Cholinergic precursor, 40% choline by weight
- Bacopa Monnieri: Memory enhancement, stress reduction
- Rhodiola Rosea: Adaptogen, fatigue reduction
Other related problems I am exploring:
- Effectiveness / difference in usage of microneedles for compounds delivery vs traditional pills, which go through digestive tracks.
- Genetic neurotypes
- Non-invasive ways to measure neurotransmitter levels in humans.
- Modalities to measure neurotransmitter levels in-vivo in mice and monkeys.
- Exploration of monkey brain tissue and keeping it alive for longer than 4 hours (current state of the art in research) - requires "brain in the jar technology" - think the CL1 from Cortical Labs but with vascularization.